Rabies is an infectious disease of viral etiology, common to all species of warm-blooded animals and transmissible to humans.
Rabies in dogs is characterized by acute manifestations expressed by nerve hyperexcitability and aggressiveness followed by paralysis and death. This disease was identified in antiquity. The Greek word “lyssa” means madness and it was first used to denominate this affection.
Rabies is a word that comes from Latin and has a very close significance to the one in Greek, namely violence.
In other words, rabies is a type of violent madness that is completely incurable, but which can be prevented. Virtually extinct, rabies is still a major public health problem in many countries on the Asian and African continents.
A history of rabies from ancient to present times
Rabies has been known since ancient times. Documents written by Homer, Aristotle, and Democritus contain information about it and its clinical forms.
In 1881, Pasteur and Roux determined that rabies is found in the central nervous system of sick animals and those that already died because of it. The pathogen agent could not be seen under the microscope and could not be replicated in synthetic conditions, so that is why it was called the “rabies virus”.
Subsequently, Pasteur developed the first scientific rabies immunization method using a strain of the rabies virus and testing it on rabbits. As a result of his research and experiments, rabies treatment was applied for the first time in 1883 in dogs and in 1885 in humans.
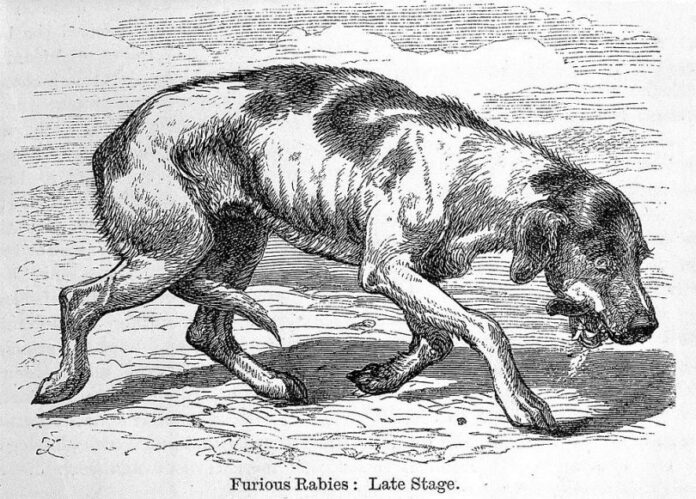
Rabid animals pose a danger to both humans and other animals. Rabies is considered the most serious zoonosis. A zoonosis is a contagious disease that can be transmitted from human to animal and the other way around.
The frequency of this disease varies from one species to another, but it is most often found in dogs. Natural sources of infection are represented by rabid animals that present symptoms of rabies, but also by rabid animals that do not show any clinical signs of disease.
Dogs may get infected by foxes, wolves, cats and rats, depending on the environment where they live. Theoretically, rabies should not be present in developed cities. It should only be carried by wild animals that live in the wilderness and do not have contact with domestic animals or with humans too often.
The mode of contamination with rabies from one animal to another or from animals to humans is directly through bites or scratches produced by diseased animals. There are, however, quite rare possibilities of indirect contamination through objects that might have come in contact with virulent material from a sick animal.
Even if there are no obvious wounds that could be detected by the naked eye, the contamination is still possible as long as the virus can penetrate a dog’s skin or a person’s skin. Therefore, this virus is not easy to avoid if it is present in peoples living environments.
Causes and factors of rabies
In order to better understand rabies, you must know that it is part of a category called Lyssavirus, which, in turn, is part of the Rhabdoviridae family. Among the classical rabies viruses, 2 types can be distinguished, namely the street rabies virus and the fixed rabies virus.

The first type designates a virus recently isolated from animals, which has not undergone any changes in the laboratory.
It is characterized by an extremely variable incubation period that is sometimes very long and the ability to invade the salivary glands. A fixed virus is characterized by a short incubation period of 4 to 6 days and it does not invade the salivary glands.
Frequency of rabies
Rabies is found in 2 natural cycles, which are the sylvatic cycle and the urban cycle. Most cases in humans are found in cities and are determined by a dog’s bite.
Rabies is not considered a public health issue because it does not generate deaths except in Asia and Africa.
A part of this aspect is given by the fact that people are aware of what a dog bite or a cat bite can do to them and they are knowledgeable enough to know what to do in case they are bitten.
As for the sylvatic cycle, natural infection is more frequent and the deaths of animals are frequent too. Among the animals that could carry the rabies virus and that live in the wilderness are foxes, wolves, coyotes, bats and so on. Rats also represent a reservoir of the virus and they might affect some urban areas as well.
Transmission of rabies
In case of rabies, transmission could be via bite, through saliva. Animals that are infected, but do not show any signs of illness can still eliminate the rabies virus 10 to 14 days prior to manifestation.

When a dog or another animal already show symptoms, their bite is even more dangerous, especially when the bite is deep and when they leave a larger quantity of saliva on the wound they create.
Moreover, scratches can also provide virus inoculation because a dog’s nails are most definitely covered in its saliva because dogs frequently lick themselves.
Unlike dog bites, cat bites are even more dangerous because their teeth are sharper and they usually penetrate one’s nerves.
Among the other ways rabies can be transmitted are through placenta, accidentally in laboratories, by corneal transplants and by airway, from bats. These cases are, of course, rare.
Clinical picture of rabies in dogs
The occurrence of symptoms of rabies in dogs or other animals marks an evolutionary stage of the disease that is often fatal. The rabies virus attacks and damages the central nervous system of a dog or other animal that includes both the brain and the spinal cord.
In order to prevent the occurrence of any symptom, rabies should be treated right after suspecting a dog or some other animal might be infected. The first symptoms can occur in a range between a few days and almost a year, but in most cases symptoms develop in 4 to 6 weeks from the time of infection.
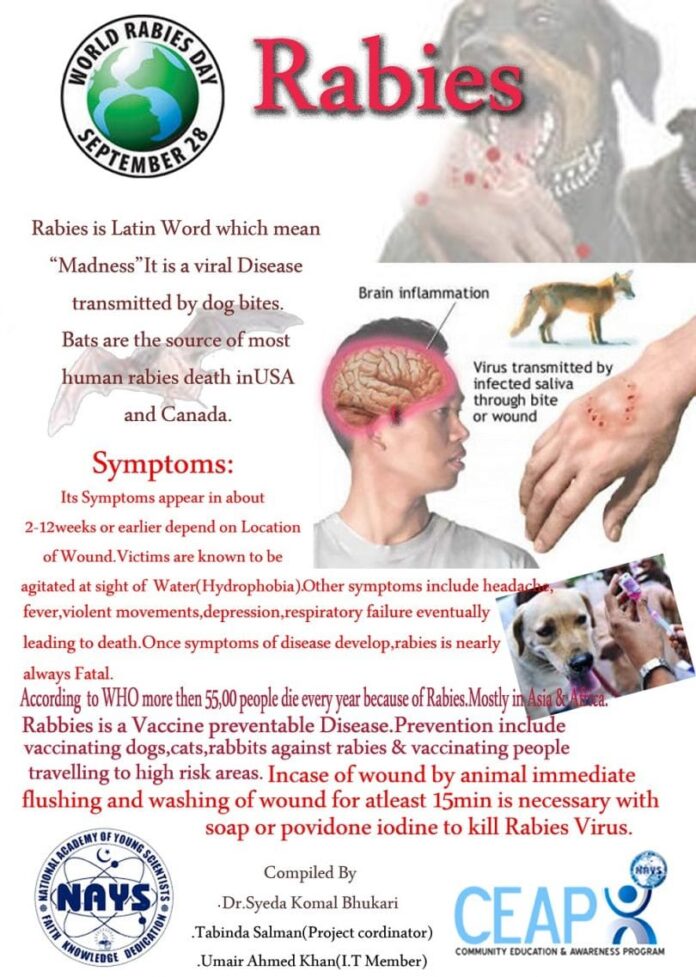
Infected animals can exhibit noticeable symptoms or behavioral disorders. An animal that has bitten a person and starts behaving strangely may be infected with rabies.
In case a dog bites a person, it is important to keep it under observation in order to provide appropriate treatment in a timely manner to anyone who came in contact with the animal and to the person who was bitten.
If a wild dog lacks fear of people, it is restless and aggressive and it suddenly changes its behavior, then it is most probably infected. A dog may also drool excessively, so be aware not to come in contact with its saliva.
Phases of infestation with rabies
The prodromal phase often goes unnoticed. The dog gets cranky, irritable, more affectionate towards its masters, or on the contrary, sad, isolated, and retreats to dark corners of the house.
The states of dereliction and anxiety suddenly succeed without reason and the dog begins to move continuously and has an exaggerated reaction to noise, light, and touch. In some cases, the dog might have auditory and visual hallucinations and trouble focusing on its owner.
Its attention may be retained only for a very short time. Appetite, preserved at the beginning, gradually diminishes and the dog begins to swallow inedible objects. As for thirst, it might be preserved or exaggerated.
Sometimes, the area around the bite becomes very itchy and the dog might scratch itself excessively. The duration of this phase is between 1 and 3 days, during which the dog’s voice might become thicker.

The angry phase is recognizable when the dog becomes aggressive especially to other animals and gets really angry because of no particular reason. It might bite hard objects, fact which could lead to breaking its teeth and even its jaw.
The dog also has a tendency to run away from home and travel large distances without any target. There are also changes in the dog’s voice, just like during the first phase.
Among the other symptoms that can be manifested by a dog going through this phase are vomiting and bloody diarrhea. It usually lasts between 2 to 6 days.

The paralytic phase is the last one that precedes death. The dog cannot move, keep its mouth closed, and so on. The paralytic phase begins with a state of depression that is quickly followed by pharyngeal and masseter muscle paralysis.
Its face expresses sadness, and suffering and it looks absent and lost. As it becomes more and more paralytic, paraplegia occurs too. The dog becomes unable to move at all. Death occurs by suffocation in less than 5 days. This phase usually lasts between 1 and 3 days and death comes amid a generalized paralysis after 3 to 4 days.
The clinical picture of rabies in humans
The typical incubation period of rabies in humans is 4 to 6 weeks. Usually, there are no obvious symptoms of this disease during this period. Early symptoms include pain and numbness around the bitten area, followed by vague signs such as fever, cough or dry throat, pain, abdominal pain, or anxiety that gets worse and can lead to extreme agitation.
Other symptoms can include alternating periods of normal behavior or unusual and bizarre behavior, such as anxiety, hallucinations, delirium, fear of water, fear of air, and muscle spasms at the face, neck, or diaphragm level.
These signs can be followed by convulsions, paralysis, large fluctuations in body temperature, pulse, and blood pressure, coma, heart failure, and respiratory failure too.
Diagnosing rabies in both dogs and humans
In humans, the diagnosis of rabies is based on specific symptoms and the person’s medical history in relation to the circumstances in which he or she was bitten.
This disease can be confused with encephalomyelitis, polio (paralytic form), tetanus (contractures and muscle movement), and delirium tremens (chronic alcohol disease). Therefore, laboratory examination is needed even if that person was obviously a victim of a dog bite.

As for dogs and other animals, they must be isolated and kept under control for 10 days during which the bitten person may also have the test results back and already know if he or she carries the virus or not.
The current method of diagnosis of rabies in animals is by microscopic examination of the subject’s brain. Some techniques for testing using samples of skin and / or blood are studied and used in some research that promises to become a new way of testing both people and animals that could be exposed. They are not commonly used at present.
Treatment options for rabies
The basic principle is for the vaccine to reach a person’s central nervous system and a dog’s central nervous system before the virus does.
The treatment is usually made with the help of an anti-rabies vaccine and serum, followed by local treatment of the wound consisting in washing it, disinfecting it with alcohol after washing it with antibacterial soap, and applying other ointments depending on how serious the wound is.
People who choose to make an anti-rabies vaccine and were not bitten are usually those working for veterinary clinics where they are exposed daily to the possibility of contamination.
Preventing contamination with rabies
The only method of prophylaxis of rabies is vaccination against rabies. In dogs, rabies vaccination is required by law and must be repeated annually.
It is good to know that the period of validity of the rabies vaccine starts only one month after vaccination. If your pet has come in contact or it was bitten by a suspect animal, you should immediately take it to the veterinarian.
Also, if you have been bitten by an infected or suspect animal, you should see a doctor as quickly as possible.
Rabies in humans can be cured as long as the treatment begins before the virus starts incubating, in a period shorter than 3 weeks. All warm-blooded animals can contract the rabies virus, but dogs and cats are most prone to it.
Avoid animal bites by doing the following:
- Do not interfere in dog fights or other animal fights
- Do not disturb animals while they are eating
- Never leave a child alone with an unknown dog or other animal
- Do not let children approach or play with wild animals of any kind
- Avoid all dogs you do not know
- All dogs and cats held in a house or a yard should be vaccinated regularly against rabies under veterinary supervision and must not come into contact with wild animals
- If bitten, do not try to catch the animal that has bitten you. Call specialized services to avoid a second bite.
The contribution of the population and the public authorities is also very important in preventing contamination with the rabies vaccine. Each dog or cat owner should vaccinate their pets.
In addition, authorities and local governments must contribute to taking effective measures in order to reduce the number of unvaccinated animals or restrict the access of wild animals in highly populated areas.

Efforts made by medical institutions and veterinary specialists in this regard are meant to increase public awareness. On the other hand, in the countries in Asia and Africa the situation is horrible and people are actually dying because of rabies.
Approximately 95% of all people who died because of being contaminated with the rabies virus are from the aforementioned continents.
World Rabies Day is a global campaign meant to increase awareness regarding rabies and to disseminate information about rabies prevention. It is celebrated every year on September 28th, the day when Louis Pasteur died.
This commemoration was established in 2007 and is designed to draw the attention of the general public.
Refresher conclusions about rabies
Once contacted by a person, this disease begins with sensations of pain, itching, tingling, headache, excitability, insomnia, sometimes sadness, lack of appetite, vomiting, hallucinations, fever, and fear of light.
It is characterized by nervous excitement and constriction of the larynx and pharynx that lead to hydrophobia and aerophobia. The symptoms last on average 3 to 6 days until death occurs without exception because of respiratory failure or cardiorespiratory failure.
When contacted by a dog or other animal, it might go through 3 phases, out of which only the second one becomes obvious. Signs are furiousness, restlessness, and desire to run away. Those that precede death are paralysis and paraplegia.

You can help too by vaccinating your pets, transmitting information about rabies to your acquaintances and friends, volunteering for events and campaigns to prevent rabies, donating to the cause, participating in events dedicated to World Rabies Day, and so on.
Although most people from civilized countries are informed and know what to do in case they get infected with rabies, there are still exceptions and parts of the world where rabies is causing deaths of people, not to mention deaths of countless animals of all kinds. Rabies is a very serious affection that can be fatal for both you and your dog.
